What is LoRaWAN®?
The LoRaWAN® specification is a Low Power, Wide Area (LPWA) networking specification designed to wirelessly connect battery operated ‘things’ to the internet in regional, national or global networks, and targets key Internet of Things (IoT) requirements such as bi-directional communication, end-to-end security, mobility and localization services.
LoRaWAN operates in unlicensed radio frequency bands and is known for its long-range capabilities (up to 15 km in rural areas), low power consumption, and the ability to connect a large number of devices to a single network. The architecture includes end devices, gateways, network servers, and application servers, enabling a scalable and flexible network for diverse IoT applications.
Why Choose LoRaWAN®?
Applications of LoRaWAN®
The applications of LoRaWAN are endless. With its robust and scalable infrastructure, LoRaWAN enhances operational efficiency and data collection, facilitating improved resource management, remote monitoring, and automation across numerous industries. A few key markets include:

Smart Buildings
Allows building managers, owners, tenants and service providers to manage building functions remotely.

Smart Industry
Streamline operations to better manage resources, equipment, safety and the environment.

Smart Logistics
Ushering in a new era of end-to-end supply chain monitoring over long distances at low cost.
Getting Started with LoRaWAN®
Dive into the essentials of LoRaWAN architecture and discover how to begin your IoT journey. Review detailed specification documents and guides to master the implementation and optimization of LoRaWAN technology for your projects.
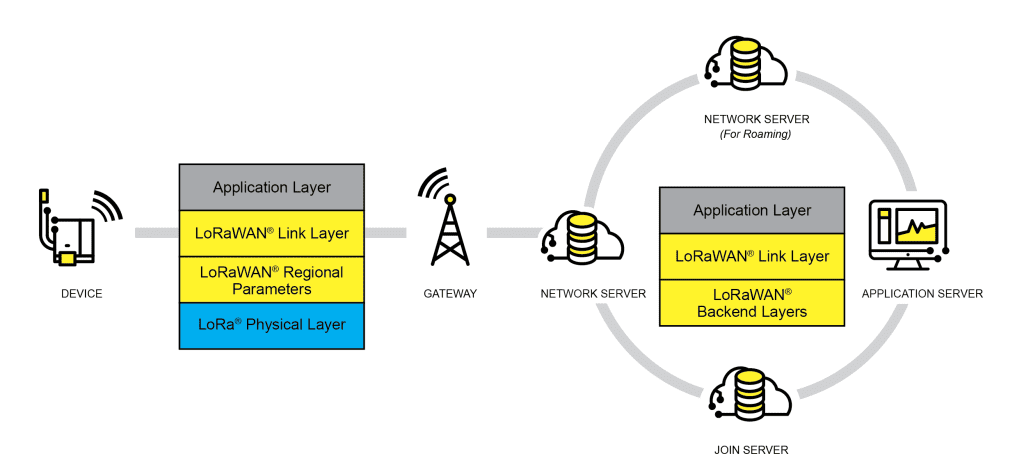
LoRaWAN® Architecture
The LoRaWAN® network architecture uses a star-of-stars topology, where gateways relay messages between end-devices and a central network server. Connected via standard IP connections, gateways convert RF packets to IP packets and vice versa. The LoRa® physical layer’s long-range capability allows single-hop links between end-devices and gateways. The system supports bi-directional communication and multicast addressing for efficient spectrum use during tasks like Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA) upgrades.
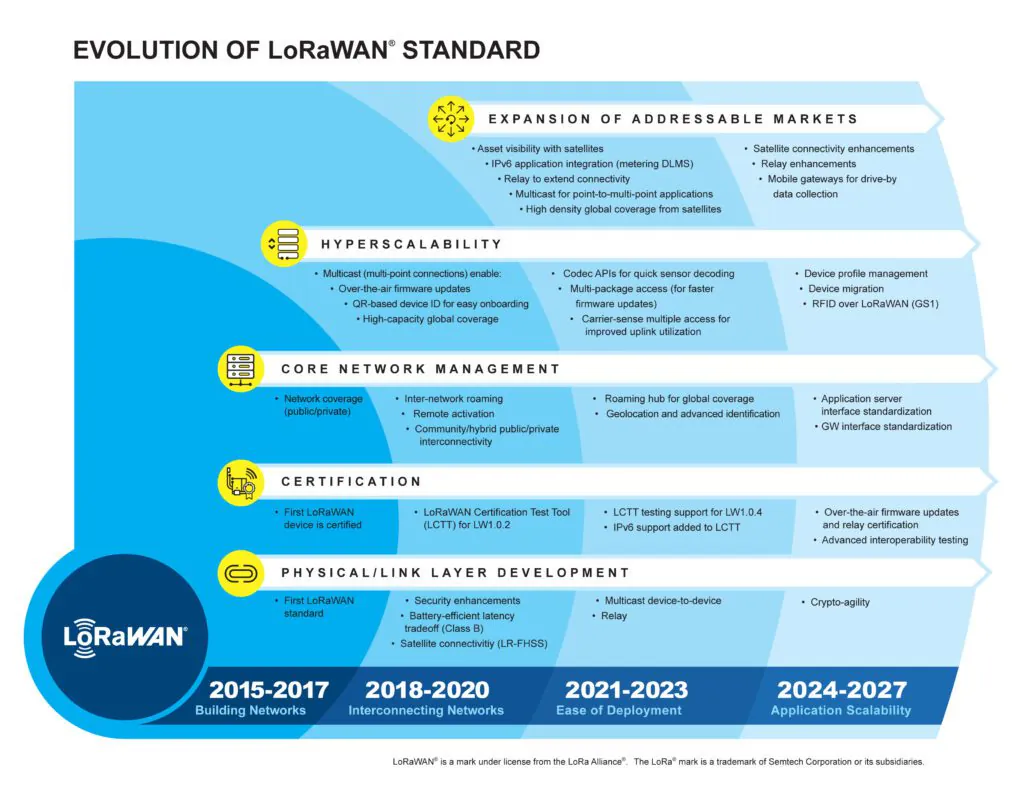
Evolution of LoRaWAN® Standard
The LoRaWAN® Evolution Roadmap highlights LoRaWAN’s evolution from building and interconnecting networks through its focus on making the technology faster and easier to deploy, work that has successfully made LoRaWAN the leading LPWAN with the most deployments supporting IoT’s active scaling across numerous end markets. The roadmap also showcases the planned development of the LoRaWAN open standard for IoT communications.
LoRaWAN® for Multi-Technology IoT Deployments
LoRaWAN operates independently, providing robust connectivity for IoT deployments. Additionally, it complements other technologies, enhancing the overall strength and versatility of IoT systems.
Learn more about how LoRaWAN complements other technologies in the FAQs at the bottom of this page.
LoRaWAN® Device Certification
LoRaWAN certification is crucial for ensuring device interoperability, reliability, and security. It guarantees compliance with industry standards, fostering trust and enabling seamless integration of IoT solutions across various applications. Learn how to get your devices ready for certification below.

Join the Ecosystem
Join the LoRa Alliance® to boost your business with access to developing the LoRaWAN specification, industry connections, and collaborative opportunities.
Gain access to a wealth of resources including technical specifications, reference designs, market reports, educational materials, marketing content, and sales resources.
Latest LoRaWAN® Specification Documents
LoRaWAN® FAQs
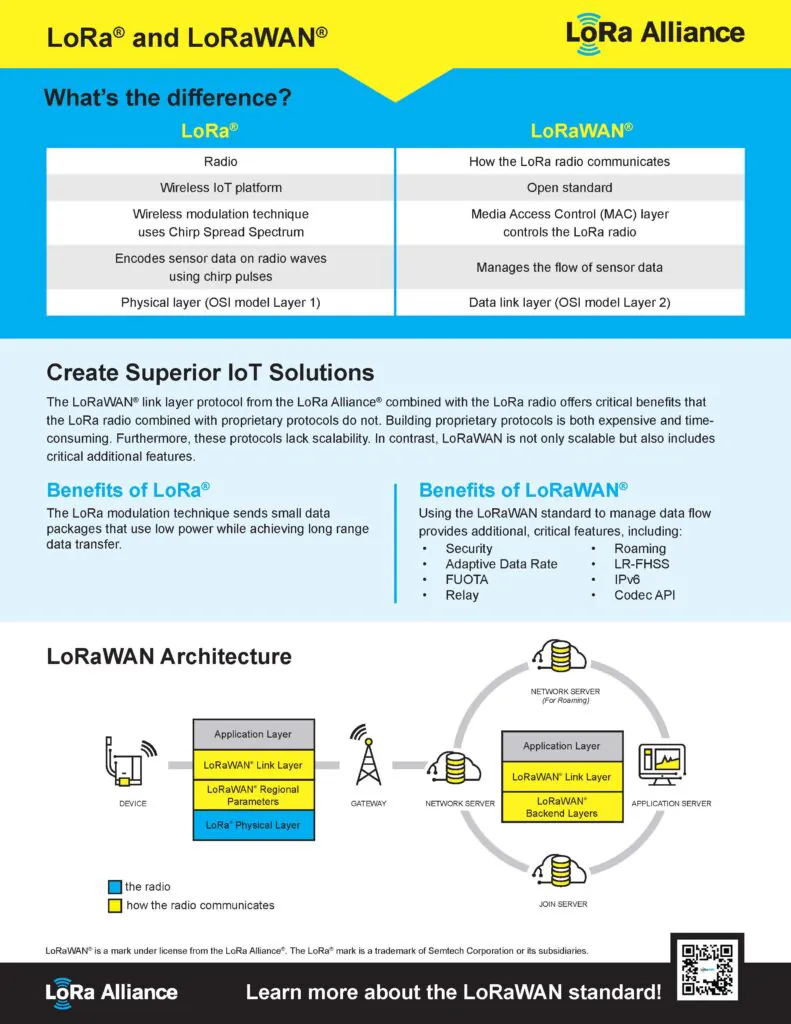
LoRa and LoRaWAN are related but serve different functions within wireless communication networks. Here are the key differences:
- Definition:
- LoRa (Long Range): Refers to the physical (PHY) layer, which includes the modulation technique used for long-range, low-power communication. LoRa is the radio signal that transmits the data over the air using spread spectrum technology.
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network): Refers to the network standard and system architecture for managing communication between LoRaWAN devices and the network server. It defines the communication standard and system architecture at the MAC (Medium Access Control) layer.
- Function:
- LoRa: Ensures long-distance communication and robust data transmission using Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) modulation. It is responsible for the low-level radio transmission.
- LoRaWAN: Manages device communication, data rates, and battery life, overseeing how data is sent and received, including security, data integrity, and the overall network structure.
- Scope:
- LoRa: Deals with the physical transmission of data over the air. It is concerned with the signal characteristics and the method of transmitting data.
- LoRaWAN: Encompasses the entire network stack, including network management, communication protocols, and application interfaces, ensuring data is properly routed and devices are managed efficiently.
- Components:
- LoRa: Focuses on LoRa chipsets and their ability to transmit data to the cloud over long distances using minimal power.
- LoRaWAN: Includes end-devices, gateways, network servers, and application servers, coordinating how data is relayed, managed, and utilized across the network.
- Security:
- LoRa: Does not include security mechanisms; it is purely a physical layer technology.
- LoRaWAN: Implements security measures like encryption and device authentication to protect data integrity and privacy.
LoRaWAN is the network protocol that links the LoRa signal (sensor data) to the application(s). To put it simply, LoRa is the radio signal that carries the data, and LoRaWAN is the communication protocol that controls and defines how that data is communicated across the network.
LoRaWAN complements 5G technology by providing a cost-effective, low-power, and long-range solution for IoT applications, making it ideal for rural or remote areas where 5G coverage might be limited. While 5G excels in high-speed, low-latency scenarios like autonomous vehicles and real-time video, LoRaWAN is better suited for low-bandwidth, infrequent data transmission such as environmental monitoring and asset tracking. Combining both technologies creates a comprehensive IoT ecosystem that leverages LoRaWAN’s scalability and energy efficiency with 5G’s high throughput and real-time capabilities, ensuring robust and versatile connectivity across various applications.

No single technology can address all IoT requirements. Learn how LoRaWAN and Bluetooth work together, and how LoRaWAN builds upon Bluetooth’s strengths in this white paper linked below.
LoRa Alliance members describe how LoRaWAN deployments complemented Bluetooth solutions and were able to:
- Extend the battery life of end-devices
- Expand the range of connectivity
- Scale the number of end-devices in use
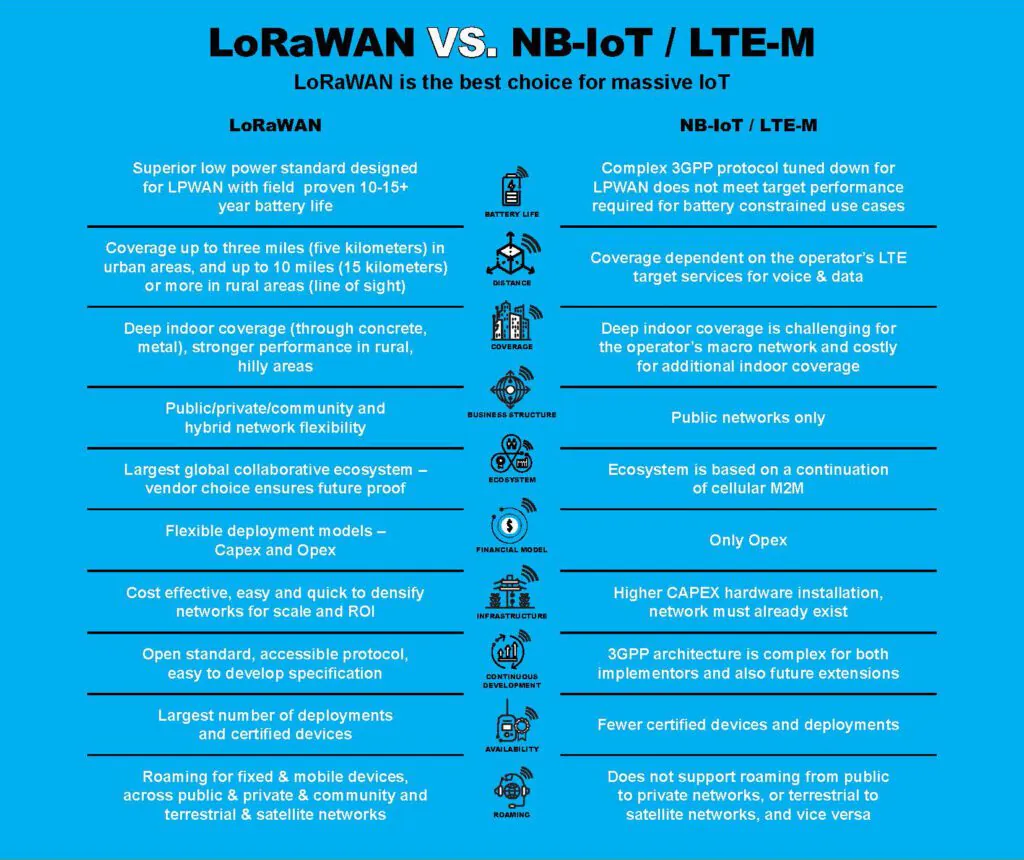
Choose LoRaWAN over NB-IoT for a more cost-effective and flexible solution, particularly for applications like smart cities, utilities, industry, and agriculture. LoRaWAN allows for private network deployments, operates on unlicensed spectrum, and offers extensive range and coverage, especially in rural areas. It supports long battery life and can handle many devices per gateway, making it highly scalable. While NB-IoT may offer higher data rates and lower latency, LoRaWAN’s benefits in terms of cost, scalability, and deployment flexibility make it the preferable choice for many IoT applications.
Wi-Fi® and LoRaWAN® are two of the most adopted unlicensed technologies and together they address a large proportion of IoT use cases. The approaches for these technologies are on the disruption of private-public business models and also enabling participation in 5G success.
The Wi-Fi & LoRaWAN® Deployment Synergies white paper intends to demonstrate how these two widely deployed IoT Connectivity technologies can be utilized in tandem to effectively support a vast array of use cases. This paper will summarize the strengths of each technology, their individual positions in the IoT ecosystem, state their complementary nature, the way that both technologies can be easily deployed simultaneously and provide testimonials.
LoRaWAN is secure by design. LoRaWAN features integrated end-to-end security implemented across multiple levels of
the standard.
The LoRa Alliance has always kept security front and center in its development of the LoRaWAN specification, which has been designed from the outset with security as an essential aspect, providing state-of-the-art security properties that meet the needs of highly scalable low-power IoT networks.
LoRaWAN’s versatility fuels the continuous expansion of its use cases, as its adaptable nature proves invaluable across diverse industries and applications, driving innovation and enabling new opportunities for connectivity and data-driven solutions.
See hundreds of use cases and case studies from real life LoRaWAN deployments.